UX Design and Psychology
UX design serves as a vital differentiator for businesses aiming to distinguish themselves in the market, as it boosts user satisfaction and engagement by enhancing usability, accessibility, and product interaction. By integrating psychological principles, UX designers can craft products that are not only functional but also profoundly engaging and impactful, establishing designs that connect with users on a deeper emotional level.
The convergence of psychology and UX design spans multiple design components, such as user research, information architecture, interaction design, and usability testing.
Understanding User Psychology
People frequently make decisions driven by recognizable psychological patterns, and this phenomenon is equally relevant in the digital realm. A crucial element of crafting an optimal user experience is having a deep understanding of your users. Ultimately, you are designing products and experiences tailored to them.
Although you can’t physically enter your users’ minds, you can skillfully leverage user psychology to grasp how users engage with and perceive your product.
Understanding User Psychology
People frequently make decisions driven by recognizable psychological patterns, and this phenomenon is equally relevant in the digital realm. A crucial element of crafting an optimal user experience is having a deep understanding of your users. Ultimately, you are designing products and experiences tailored to them.
Although you can’t physically enter your users’ minds, you can skillfully leverage user psychology to grasp how users engage with and perceive your product.
Emotional influences on user behavior
Another crucial aspect of user psychology in UX design is the emotional impact on user behavior, which shapes how users respond to a design and how those emotions affect their decisions. Don Norman, often regarded as the Godfather of UX, highlights in his book Emotional Design: Why We Love (or Hate) Everyday Things that while functionality is important, it’s the emotional connection that truly makes a difference.
He asserts that products that elicit positive emotions—such as pleasure, excitement, or satisfaction—are significantly more effective in engaging users and fostering long-lasting positive associations.
For instance, if your travel booking website allows users to experience the thrill of exploring beautiful destination photos, provides intuitive filters for finding the ideal getaway, and sends a confirmation email with a polished and personalized itinerary, this user journey, designed with emotional considerations, fosters feelings of control, trust, and excitement. This ultimately influences the user’s decision to select your platform for their travel needs.
On the other hand, a website that features disorganized navigation, unexpected fees, and a cumbersome checkout process can trigger feelings of frustration and distrust, prompting users to abandon their purchases altogether.
Emotional Design Principles
To maximize the emotional impact on your users, it is essential to employ emotional design principles that evoke specific feelings through your interfaces. These emotions can significantly influence user behavior, foster positive associations with the product, and ultimately contribute to a more satisfying user experience.
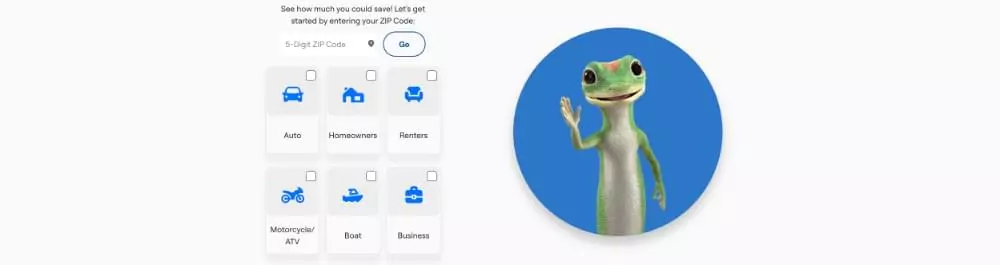
A prime example of this is GEICO Insurance, which features a gecko as its mascot. This whimsical character immediately captures users’ attention, transforming a mundane experience into one filled with delight and subtly enhancing the chances of user engagement by eliciting positive emotions.
Here are several ways to implement emotional design and enhance the user experience:
Utilize Visual Elements: Use colors, images, and layouts to establish the desired mood. For example, incorporating calming visuals in a banking app can foster a sense of security and trust.Create Micro-Interactions: Implement subtle animations and feedback sounds to evoke feelings of delight or satisfaction. Progress bars and celebratory sounds indicating task completion can enhance the user experience.Make Use of Storytelling: Employ storytelling techniques to emotionally engage users. Sharing narratives about how your product or service has positively impacted other users can foster empathy and trust.Use Humorous Messages: Integrate playful or humorous messages throughout the user experience, particularly in error notifications, to lighten the mood and alleviate frustration.Leverage Social Proof: Highlight positive user testimonials and reviews to build trust and credibility, strengthening the emotional connection with your brand.
User-Centric Design Principles
User-centric design (UCD) principles ensure that the design process focuses on creating products and experiences that prioritize the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users. By emphasizing the user throughout the design process, UCD helps create designs that are intuitive, accessible, and engaging for the target audience.
While user involvement, consistency, and simplicity are fundamental to user-centric design, here are additional principles to consider for crafting a successful user experience.
Usability and Accessibility
Improving the usability and accessibility of your products ensures they can be utilized by the broadest audience possible, including individuals with disabilities or limitations. With approximately 1.3 billion people worldwide experiencing some form of disability, enhancing usability and accessibility presents a significant opportunity to reach this extensive user base.
This principle involves creating interfaces that are easy to navigate, comprehend, and interact with, regardless of a user’s background or abilities.
The Importance of Intuitive Navigation
Intuitive navigation is essential for allowing users to easily find and access the information they need within your product. It entails designing menus, links, and other navigation elements in a logical and comprehensible manner.
Intuitive navigation further enhances your UX design by helping you:
- Reduce Friction: Clear and straightforward navigation minimizes the mental effort required for users to locate what they’re looking for, alleviating frustration and keeping users engaged.
- Improve Conversion Rates: Intuitive navigation increases the likelihood that users will complete desired actions, such as purchasing a product or subscribing to a service.
- Reduce Support Costs: By enabling users to find answers independently, intuitive navigation can decrease the need for user support, thus lowering operational costs.
Inclusive Design Practices
Inclusive design practices involve creating products and experiences that cater to a wide range of abilities and disabilities. Research indicates that by accommodating diverse needs, you can potentially expand your customer reach by four times.
Here’s how to implement inclusive design practices to make your products more accessible and user-friendly for everyone:
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all functionalities can be accessed using only the keyboard. This is crucial for users with motor limitations or those who rely on screen readers.
- Color Contrast: Maintain a clear contrast ratio between text and background colors. This is particularly beneficial for users with visual impairments, including those with color blindness.
- Descriptive Text Alternatives: Provide alternative text descriptions for images and non-text content. This aids users who rely on screen readers or have difficulty interpreting visuals.
- Resizable Text: Allow users to adjust text size according to their preferences. This feature supports users with visual impairments or reading difficulties.
- Subtitles and Captions: Include subtitles or captions for video and audio content. This practice benefits users who are deaf or hard of hearing, as well as those learning a new language.
- Multiple Input Methods: Offer various input options beyond just a mouse or touchscreen. Consider incorporating voice commands or gesture controls for users with limited dexterity.
- User Testing with Diverse Groups: Conduct beta testing with a diverse range of participants, including individuals with disabilities. This approach helps identify and address accessibility issues early in the development process.
Visual Hierarchy and Information Architecture
Visual hierarchy and information architecture function like organized sections and labeled shelves in a library, guiding users to easily locate what they need. These principles work together to:
- Organize Information for User Clarity: Imagine a recipe book with distinct sections for appetizers, main courses, and desserts. Each recipe includes a list of ingredients and step-by-step instructions, making it straightforward to follow. In UX design, organizing information aids users in navigating content more efficiently and comprehending it more effectively. This can be achieved through:
- Headings and Subheadings: These guide users to specific categories of information.
- Bullet Points and Numbered Lists: These formats make information scannable and easily digestible.
- White Space: Adequate spacing prevents visual clutter and enhances readability.
- Prioritize Key Elements for Effective Communication: In a well-designed store, key products are prominently displayed to capture attention and convey their significance. Similarly, in UX design, prioritizing essential elements directs users’ focus toward crucial information, such as important messages, calls-to-action, or vital features, ensuring they are easily noticed and understood. This can be accomplished by using:
- Bold Text and Larger Font Sizes: These draw attention to important information.
- Contrasting Colors: These visually distinguish different types of content.
- Call-to-Action Buttons: These act as prominent indicators that guide users to take specific actions, such as “Subscribe” or “Learn More.”
Behavioral Design Techniques
Behavioral design patterns are powerful strategies that can influence user behavior and encourage specific actions or interactions. These techniques draw from principles of behavioral psychology and behavioral economics, which examine how individuals make decisions and behave in various contexts.
For instance, a shopping website might leverage the principle of scarcity by displaying messages such as “Only 2 items left!” This approach creates a sense of urgency, prompting users to make quicker purchase decisions.
Nudging and Persuasion
Nudging and persuasion are crucial elements of behavioral design techniques aimed at subtly guiding users toward desired actions. These methods encourage specific choices or behaviors without restricting the user’s freedom of choice.
According to BJ Fogg, Director of the Stanford Behavior Design Lab, behavior occurs when three elements converge: motivation, ability, and trigger. If a desired behavior doesn’t take place, it often indicates that one of these components is lacking.
This model assists designers in identifying barriers that hinder user actions and provides a framework for diagnosing issues related to:
- Core Motivators: Understanding what drives users to take action.
- Simplicity Factors: Making tasks easy and accessible.
- Prompts or Triggers: Utilizing timely reminders to prompt engagement.
Encouraging Desired User Actions
To motivate users to complete a survey, for example, implementing a progress bar can foster a sense of accomplishment and encourage completion.
Additionally, referring back to Fogg’s model, you can enhance user motivation by emphasizing the benefits of completing the survey, such as contributing to the improvement of future products or services.
To enhance ability, ensure that the survey process is user-friendly and accessible, simplifying the steps required to complete it. Triggers can be utilized through timely reminders or notifications, nudging users to engage with the survey.
By effectively combining these elements, UX designers can significantly increase the likelihood of users completing desired actions, such as surveys or purchases.
Leveraging behavioral economics principles
You can also leverage principles from behavioral economics, including loss aversion, social proof, and the scarcity effect, to encourage users to take specific actions.
For example, an eCommerce website might utilize social proof by showcasing customer reviews and ratings, which can influence potential buyers to proceed with their purchases. Additionally, displaying messages about limited stock can create a sense of urgency, prompting users to make quicker buying decisions.
Gamification in UX
Gamification is a highly effective strategy for enhancing user engagement. It’s akin to adding a touch of magic to your user experience, turning mundane tasks into exciting and rewarding interactions. This approach utilizes game mechanics to inspire users, elevate engagement, and encourage desired behaviors:
Incorporate game elements to boost engagement. Integrating game elements like progress bars, achievement badges, and virtual rewards can significantly enhance user engagement on a website.
For instance, Duolingo, a well-known language-learning application, employs a leveling system to track user progress and encourage continued learning. By gamifying the educational experience, users are more inclined to remain engaged and motivated to meet their language-learning objectives.
Encourage user interaction with rewards. Rewards serve as a compelling incentive in gamification. Providing users with rewards for completing tasks or achieving milestones can markedly increase their engagement.
A prime example is the Starbucks Rewards program, which features a point system that allows customers to earn stars for their purchases, redeemable for complimentary drinks or food. This not only motivates customers to increase their spending but also fosters brand loyalty.
Personalization and User Empowerment
Personalization and user empowerment focus on customizing experiences and providing control options, which enhance user engagement and foster trust. Netflix exemplifies this approach by offering a unique homepage experience for each of its 260.8 million users, tailored to their individual preferences. Their exceptional ability to provide personalized recommendations has led to a remarkable increase in viewer engagement, from a modest 2% to an impressive 80%.
By personalizing interactions, you can create a more meaningful and engaging experience for your users. Here are some effective strategies:
Tailoring experiences based on user preferences
Customizing experiences can significantly enhance user satisfaction and engagement with your product or service. This not only improves the overall experience but also fosters a sense of connection and loyalty to your brand.
Utilizing user data and behavior, you can:
- Recommend relevant content and features: Present users with products they are likely to enjoy, suggest articles based on their reading habits, or personalize search results according to their past queries.
- Adapt the interface: Modify the layout, language, or even color scheme based on user preferences, creating a more comfortable and familiar environment.
- Offer personalized communication: Tailor email newsletters, marketing messages, or in-app notifications to resonate with individual users.
Providing control and customization options
Empowerment extends beyond merely personalizing experiences; it involves granting users control over their interactions. This can include:
- Customization options: Enable users to personalize their dashboards, set preferences, or choose how they wish to engage with the product.
- Transparency and control over data: Clearly communicate how user data is collected and utilized, while offering options for users to manage their privacy settings.
- Multiple pathways to accomplish tasks: Provide various methods for users to achieve the same goal, accommodating different preferences and learning styles.
Build Trust Through Transparent Personalization
Establishing trust is essential for effective personalization. Users must feel secure about how their data is utilized and assured that their preferences are honored. Here are key strategies to foster this trust:
- Be Transparent About Data Collection and Usage:
Clearly communicate what data is being collected, how it will be used, and who will have access to it. Providing this information upfront helps users understand the rationale behind data usage. - Offer Clear Opt-Out Options:
Empower users by allowing them to choose whether they want their data used for personalization. Providing straightforward opt-out options demonstrates respect for user autonomy and privacy. - Focus on the Benefits:
Effectively communicate how personalization enhances the user experience and adds value. Highlighting the advantages of tailored interactions can help users see the positive impact of sharing their data.
Case Studies: Effective UX Strategies
Successful UX design strategies effectively address user needs and expectations while aligning with business goals. Here are some examples of companies that have implemented UX design strategies leveraging psychological principles to enhance user experience:
Amazon’s One-Click Ordering
Amazon utilizes Loss Aversion, a principle from behavioral economics, in its one-click ordering system. This approach reduces the perceived effort involved in making a purchase. By making the buying process seamless, Amazon capitalizes on users’ psychological tendency to act quickly to avoid missing out on products.
LinkedIn’s Profile Strength Meter
LinkedIn employs the Goal Gradient Effect, which suggests that people are motivated to complete a goal as they perceive themselves getting closer to it. The profile strength meter visually indicates progress, encouraging users to fill out their profiles fully and boosting engagement and completion rates.
Apple’s Minimalist Design
Apple’s commitment to minimalist design reflects Sweller’s Cognitive Load Theory, which posits that humans have a limited capacity for processing information. By reducing clutter and extraneous elements, Apple minimizes cognitive load, allowing users to focus on essential features and engage more deeply with the core functionalities of their products.
Case Studies: Ineffective UX Strategies
Here are some interesting instances where companies implemented UX design strategies that didn’t resonate with users, along with the insights gained.
Snapchat’s App Redesign
In 2018, Snapchat underwent a redesign of its app to distinguish between content from friends and content from publishers, with the goal of enhancing user engagement. However, this overhaul sparked significant backlash from users, who found the new interface confusing and less user-friendly. Consequently, Snapchat experienced a decline in its user base and a drop in overall engagement.
Learning: It’s crucial to avoid drastic redesigns and adhere to Weber’s law, which posits that the just-noticeable difference between two stimuli is proportional to their magnitude. In UX design, this implies that gradual, incremental modifications are typically more effective and better received by users compared to sudden and radical redesigns.
Google+ Auto Subscription
In 2011, Google+ implemented an automatic subscription feature that enrolled users in the Google+ profiles of their Gmail contacts. This approach was perceived as intrusive and a violation of user privacy. The lack of transparency surrounding this decision, combined with the failure to resolve security vulnerabilities that compromised user privacy, led to significant negative media coverage and user complaints. Ultimately, this contributed to the platform’s failure and its shutdown in 2019.
Learning: It is essential to uphold user autonomy and privacy by clearly communicating data practices. Providing users with control over their information and preferences fosters customer loyalty and helps mitigate backlash.
Airbnb “Trips” Feature
In 2016, Airbnb introduced the “Trips” feature, designed to be a comprehensive solution for booking various travel experiences alongside accommodations. However, users found the interface to be cluttered and confusing, resulting in the feature failing to gain popularity.
Learning: Always conduct user testing to ensure that new features align with existing user behaviors. It is crucial to thoroughly understand user needs and behaviors before introducing new functionalities. Additionally, present information in manageable chunks, following Miller’s law, which suggests organizing information into groups of around 7 items (plus or minus 2). This approach aids users in navigating and processing information more effectively, thereby enhancing the overall user experience.
Testing and Iteration in UX Design
Testing and iteration are essential components of the UX design process, ensuring that design elements are centered around user needs and effective in function. By involving users early and frequently, you can gain invaluable insights into how they interact with your designs, understand their requirements and pain points, and pinpoint areas needing improvement.
For example, Spotify consistently tests new features with a select group of users before wider release. This iterative strategy enables Spotify to collect feedback, refine features, and ultimately enhance the user experience.
Importance of User Testing in Validating Design Choices
User testing is vital for confirming your design assumptions before they lead to costly mistakes. Consider the scenario of investing months developing a feature only to discover later that users find it confusing or unhelpful. User testing helps you avoid such pitfalls by enabling you to:
- Identify Usability Issues: Observing user interactions reveals problems such as unclear labels, confusing navigation, or inefficient workflows. For instance, a user testing session might uncover that users have difficulty finding the search bar due to its poor placement or lack of visual prominence.
- Evaluate User Understanding: Testing assesses whether users grasp the design’s purpose and functionality. For example, it may reveal that users are unaware of key product features due to unclear benefit statements or insufficient information.
- Gauge User Satisfaction: User testing allows you to measure satisfaction levels by collecting feedback. For instance, during a mobile app test, users might express frustration with slow loading times, highlighting areas for improvement in performance.
Incorporating User Feedback for Iterative Improvements
Collecting user feedback is essential for identifying areas that require enhancement and making iterative changes to improve the user experience. Feedback can be gathered through surveys, customer experience software tools, interviews, or usability testing.
Here’s how gathering user feedback facilitates iterative improvements:
- Identify Pain Points: By conducting interviews, surveys, and usability tests, you can uncover users’ pain points and frustrations with the current design. For instance, feedback may indicate that users perceive the checkout process on an eCommerce website as lengthy and cumbersome.
- Prioritize Improvements: Based on the feedback collected, you can determine which aspects of your design need the most attention. This ensures that your efforts are focused on resolving issues that are most significant to users. For example, the eCommerce website team might prioritize streamlining the checkout process by minimizing unnecessary steps and enabling guest checkout options.
- Refine Your Design: User feedback informs you in refining your design to make it more user-friendly and intuitive. This iterative approach leads to a design that genuinely resonates with users and effectively addresses their needs.
A/B Testing for Optimization
A/B testing involves comparing two different versions of a design element to determine which performs better based on user behavior. This approach allows you to make data-driven decisions for further optimization.
For example, a news website might conduct A/B tests on two distinct home page layouts—one focused on breaking news and the other on curated content—to see which keeps users engaged longer and generates more page views.
Here are several reasons to consider A/B testing for optimization in your design systems:
- Test Specific Design Variations: A/B testing allows you to compare different versions of elements such as buttons, calls to action (CTAs), layouts, or even entire pages to test hypotheses and identify which is more effective. For instance, you might test two color variations for a “Buy Now” button to see which leads to higher conversion rates.
- Obtain Quantifiable Results: A/B testing yields quantitative data on user behavior, including click-through rates, conversion rates, and time spent on a page, enabling you to make objective decisions regarding design. For example, if a red “Buy Now” button attracts more clicks than a blue one, it suggests that the red button is more visually appealing and encourages user action.
- Continuous Optimization: A/B testing enables continuous refinement and optimization of your design based on data-driven insights. After implementing the red “Buy Now” button, you can conduct further A/B tests to optimize other website elements, such as product descriptions or promotional banners.
Ethical Considerations for User-Centric UX Design
While user-centricity is essential in UX design, it is equally important to approach it with ethical considerations in mind. Design decisions can significantly influence user behavior and well-being, and neglecting ethical principles can lead to harmful outcomes.
Here are some key areas to focus on:
- Balance Persuasion with User Autonomy: As a UX designer, you may aim to encourage users to take specific actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. However, it’s vital to respect user autonomy and avoid manipulative tactics that may pressure users into actions they are uncomfortable with. Providing clear information and choices empowers users to make decisions that align with their preferences.
- Ensure Informed Consent in UX Design: Obtaining informed consent is crucial, particularly when collecting personal data or implementing features that may affect user privacy. You should clearly communicate the purpose of data collection, how the data will be utilized, and provide users with the option to consent or opt out.
- Move Beyond Legalese: Instead of relying on complex legal terminology, present privacy policies in clear, straightforward language that minimizes ambiguity. Users should be able to understand what they are consenting to without needing legal expertise.
- Address Privacy Concerns and Data Security: Prioritizing secure data storage, encryption, and compliance with privacy regulations is essential. By communicating these practices transparently to users, you build trust and ensure ethical practices are upheld.
Future Trends in UX Design
The ever-evolving field of UX design is filled with exciting possibilities. By embracing new technologies and exploring the intricacies of human behavior, designers can craft experiences that not only satisfy user needs but also resonate emotionally with them.
This human-centered methodology has the potential to transform how we engage with technology and shape the future of user experience.
Emerging Technologies in UX Design
Here’s what is influencing the future of UX:
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): These immersive technologies require a deep understanding of user perception, spatial awareness, and emotional reactions in virtual environments. Designing for AR and VR necessitates the adaptation of psychological principles to ensure user comfort and engagement while minimizing cognitive overload.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI-driven personalization demands careful consideration of user biases, ethical concerns, and the risk of discrimination. A solid understanding of user psychology is essential to ensure that AI provides experiences that are both responsible and equitable.
- Voice User Interface (VUI): Designing for VUIs, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant, necessitates comprehension of speech recognition, natural language processing, and user intent. It’s vital to understand how users interact with VUIs and their expectations for voice communication to create intuitive experiences.
The Evolution of Psychology-Driven UX Strategies
Over the years, UX design has experienced an intriguing transformation. Initially focused on aesthetics and usability, a paradigm shift has placed psychology at the core of creating outstanding user experiences. This shift has resulted in several key trends that are shaping the future of UX design, including:
- Emphasis on Emotional Design: There will be a growing focus on crafting designs that consider users’ emotional journeys, aiming to elicit positive emotions and foster trust.
- Neuroscience and Biometric Research: Advancements in these fields will provide deeper insights into user behavior, leading to more intuitive interfaces that adapt to users’ cognitive states.
- Hyper-Personalized Experiences: By leveraging psychology and new technologies, UX design will create tailored experiences that cater to individual needs and preferences, thereby enhancing user satisfaction.
- Enhanced Human-Computer Interaction: As technology becomes more intuitive, interactions will feel increasingly natural and seamless, merging the boundaries between physical and digital realms.
Conclusion
The convergence of psychology and UX design has revolutionized our approach to user experience. By comprehending and implementing psychological principles, designers can craft experiences that are more engaging, intuitive, and impactful for users. From understanding cognitive processes to acknowledging emotional influences, psychology is integral in shaping user behavior and guiding design choices.
As we move forward, emerging technologies such as AR/VR, AI/ML, and VUIs will play a pivotal role in influencing digital UX design, providing fresh opportunities for creating innovative and personalized experiences. By embracing these trends and maintaining a focus on psychology-driven strategies, designers can develop experiences that not only fulfill user needs but also resonate on a deeper level, ultimately defining the future of user experience.